FLITECAM Redux Developer’s Manual¶
Introduction¶
Document Purpose¶
This document is intended to provide all the information necessary to maintain the FLITECAM Redux pipeline, used to produce Level 2 and 3 reduced products for FLITECAM imaging and grism data, in either manual or automatic mode. Level 2 is defined as data that has been processed to correct for instrumental effects; Level 3 is defined as flux-calibrated data. A more general introduction to the data reduction procedure and the scientific justification of the algorithms is available in the FLITECAM Redux User’s Manual.
This manual applies to FLITECAM Redux version 2.0.0.
Redux Revision History¶
FLITECAM Redux was developed as a set of software modules in the SOFIA Redux Python package:
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam: processing algorithms specific to the FLITECAM instrumentsofia_redux.instruments.forcast: image processing algorithms useful to both the FORCAST and FLITECAM instrumentsofia_redux.calibration: flux calibration algorithmssofia_redux.spectroscopy: spectral extraction algorithmssofia_redux.pipeline: interactive and batch mode interface tools for managing data reduction processessofia_redux.toolkit: numerical algorithms and supporting utilitiessofia_redux.visualization: data analysis and visualization tools
The flitecam module is a re-implementation of algorithms first
developed in IDL for the FLITECAM imaging pipelines, called FDRP.
forcast, calibration, and spectroscopy modules are based on earlier
IDL libraries called DRIP, PipeCal, and FSpextool respectively. The
pipeline module also had an earlier IDL implementation, also called Redux.
FDRP was initially developed by Dr. Ralph Shuping in 2003; its functionality was significantly improved and expanded by Dr. Sachin Shenoy in 2012. Version 1.0.0 was originally released for use at SOFIA in July 2013. FDRP originally contained a set of imaging reduction functions, and a wrapper script used both as an automatic pipeline and as a command-line interface for manual reductions.
DRIP was first developed in IDL by Dr. Luke Keller and Dr. Marc Berthoud for the reduction of FORCAST data. Version 1.0.0 was originally released for use at SOFIA in July 2013. DRIP originally contained a set of imaging reduction functions, an object-oriented structure for calling these functions, an automatic pipeline, and an interactive GUI for manual reductions. The package also supported spectroscopic reductions with an interface developed in parallel to the DRIP interface, called FG (FORCAST Grism).
PipeCal was developed by the SOFIA Data Processing System (DPS) team to provide photometry and flux calibration algorithms that may be used to calibrate imaging data from any instrument, given appropriate reference data. It was originally developed by Dr. Miguel Charcos-Llorens and Dr. William Vacca as a set of IDL and shell scripts that were run independently of the Level 2 pipeline, then was refactored by Melanie Clarke for incorporation into the Redux pipeline. It was first incorporated into FLITECAM Redux in version 1.0.1, which was released for use in May 2015.
FSpextool was built on top of a pre-release version of Spextool 4, an IDL-based package developed by Dr. Michael Cushing and Dr. William Vacca for the reduction of data from the SpeX instrument on the NASA Infrared Telescope Facility (IRTF). Spextool was originally released in October 2000, and has undergone a number of major and minor revisions since then. The last stable public release was v4.1, released January 2016. As Spextool does not natively support automatic command-line processing, FSpextool for SOFIA adapted the Spextool library to the SOFIA architecture and instruments; version 1.0.0 was originally released for use at SOFIA in July 2013.
Redux was originally developed to be a general-purpose interface to IDL data reduction algorithms. It provided an interactive GUI and an object-oriented structure for calling data reduction processes, but it did not provide its own data reduction algorithms. It was developed by Melanie Clarke, for the SOFIA DPS team, to provide a consistent front-end to the data reduction pipelines for multiple instruments and modes, including FLITECAM.
The SOFIA Redux package was developed as a unified Python package to support data reduction for all facility class instruments for SOFIA, replacing all legacy pipelines with an integrated, shared code base. The package was developed by the SOFIA DPS team, starting in 2018. The principal developers for SOFIA Redux prior to the FLITECAM 2.0.0 release were Daniel Perera, Dr. Rachel Vander Vliet, and Melanie Clarke, for the SOFIA-USRA team.
Overview of Software Structure¶
The sofia_redux package has several sub-modules organized by functionality:
sofia_redux
├── calibration
├── instruments
│ ├── exes
│ ├── fifi_ls
│ ├── flitecam
│ ├── forcast
│ └── hawc
├── pipeline
├── scan
├── spectroscopy
├── toolkit
└── visualization
The modules used in the FLITECAM pipeline are described below.
sofia_redux.calibration¶
The sofia_redux.calibration module contains flux calibration algorithms
used by Redux to perform photometric or flux calibration calculations on
input images and return their results. The complexity of this package is
primarily in the organization of the reference data contained in the
data directory. This directory contains a set of calibration data for
each supported instrument (currently FORCAST, FLITECAM, and HAWC+). For each
instrument, the configuration files are split into groups based on how
often they are expected to change, as follows.
In the filter_def directory, there is a file that defines the mean/reference wavelength, pivot wavelength, and color leak correction factor for each filter name (SPECTEL). This may vary by date only if the filters change, but keep the same SPECTEL name. The color leak factor is currently 1.0 for all filters (no color correction).
In the response directory, there are response fit files that define the fit coefficients for each filter, with a separate file for the altitude fit, airmass fit, and PWV fit for each of single/dual modes. These should also change rarely.
In the ref_calfctr directory, there are files that define the average reference calibration factors to apply to science objects, by filter, along with the associated error value. It is expected that there will be a different ref_calfctr file for each flight series, produced by an analysis of all standards taken throughout the flight series.
In the standard_flux directory, there is a file that defines the flux model characteristics for each object: the percent error on the model, and the scale factor to apply to the model. The model error is 5% for all stars except BetaPeg (which is 9.43%), and is 20% for all asteroids. The scale factor is usually 1.0, with the exception of BetaUmi, which requires scaling by 1.18 from the model output files. This file should change rarely, if ever, except to add objects to it. Currently, the same file is used for all data. Also in the standard flux directory, there are output files from the standard models for each object, for each applicable date if necessary. From these files, the lambda_mean column is read and compared to the mean wavelength in the filter_def file. If found, the corresponding value in the Fnu_mean column is used as the standard model flux. If there is a scale defined in the model_err file, it is applied to the flux value. These files should rarely change, but new ones will be added for asteroids any time they are observed. They may need to be redone if the filter wavelengths change.
To manage all these files, there is a top-level calibration configuration file (caldefault.txt), which contains the filenames for the filter definition file, the model error file, the reference cal factor file, and the response fit files, organized by date and filter. This table will most likely be updated once per series, when we have generated the reference calibration factors. There is also a standards configuration file (stddefault.txt) that identifies the model flux file to use by date and mode (single/dual). For stars, the date is set to 99999999, meaning that the models can be used for any date; asteroids may have multiple entries - one for each date they are observed. This file must be updated whenever there are new asteroid flux models to add, but it should be as simple as dropping the model file in the right directory and adding a line to the table to identify it.
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam¶
The sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam module is written in Python using
standard scientific tools and libraries.
The data reduction algorithms used by the pipeline are straight-forward functions that generally take FITS data structure, corresponding to a single image file, as an argument and return the processed data as a result. Parameters for these functions are provided as keyword arguments.
The flitecam module also stores any reference data needed by the FLITECAM
pipeline, in either imaging or grism mode. This includes
nonlinearity coefficients, wavelength calibration files,
atmospheric transmission spectra, spectral
standard models, and instrument response spectra. The default files may
vary by date; these defaults are managed by the getcalpath function
in the flitecam module. New date configurations may be added to the
caldefault.txt files in flitecam/data/caldefault.txt and
flitecam/data/grism/caldefault.txt.
sofia_redux.instruments.forcast¶
The sofia_redux.instruments.forcast module is primarily used in
the FLITECAM pipeline for its implementation of image registration and
coaddition algorithms.
Similar to the flitecam module, forcast algorithms are implemented as
straight-forward functions. They generally take a data array, corresponding
to a single image file, as an argument and return the processed image array
as a result. They generally also take as secondary input a variance array
to process alongside the image, a header array to track metadata, and keyword
parameters to specify non-default settings.
sofia_redux.spectroscopy¶
The sofia_redux.spectroscopy package contains a library of general-purpose
spectroscopic functions. The FLITECAM pipeline uses these algorithms
for spectroscopic image rectification, aperture identification, and
spectral extraction and calibration. Most of these algorithms are simple
functions that take spectroscopic data as input and return processed data
as output. However, the input and output values may be more complex than the
image processing algorithms in the flitecam package. The Redux interface
in the pipeline package manages the input and output requirements for
FLITECAM data and calls each function individually. See the
sofia_redux.spectroscopy API documentation for more information.
sofia_redux.toolkit¶
sofia_redux.toolkit is a repository for classes and functions of general usefulness,
intended to support multiple SOFIA pipelines. It contains several submodules,
for interpolation, image manipulation, multiprocessing support, numerical calculations, and
FITS handling. Most utilities are simple functions that take input
as arguments and return output values. Some more complicated functionality
is implemented in several related classes; see the sofia_redux.toolkit.resampling
documentation for more information.
sofia_redux.visualization¶
The sofia_redux.visualization package contains plotting and display
routines, relating to visualizing SOFIA data. For the FLITECAM pipeline,
this package currently provides an interactive spectral viewer and a module
that supports generating quick-look preview images.
sofia_redux.pipeline¶
Design¶
Redux is designed to be a light-weight interface to data reduction pipelines. It contains the definitions of how reduction algorithms should be called for any given instrument, mode, or pipeline, in either a command-line interface (CLI) or graphical user interface (GUI) mode, but it does not contain the reduction algorithms themselves.
Redux is organized around the principle that
any data reduction procedure can be accomplished by running a linear
sequence of data reduction steps. It relies on a Reduction class that
defines what these steps are and in which order they should be run
(the reduction “recipe”). Reductions have an associated Parameter
class that defines what parameters the steps may accept. Because
reduction classes share common interaction methods, they can be
instantiated and called from a completely generic front-end GUI,
which provides the capability to load in raw data files, and then:
set the parameters for a reduction step,
run the step on all input data,
display the results of the processing,
and repeat this process for every step in sequence to complete the
reduction on the loaded data. In order to choose the correct
reduction object for a given data set, the interface uses a Chooser
class, which reads header information from loaded input files and
uses it to decide which reduction object to instantiate and return.
The GUI is a PyQt application, based around the Application
class. Because the GUI operations are completely separate from the
reduction operations, the automatic pipeline script is simply a wrapper
around a reduction object: the Pipe class uses the Chooser to
instantiate the Reduction, then calls its reduce method, which calls
each reduction step in order and reports any output files generated.
Both the Application and Pipe classes inherit from a common Interface
class that holds reduction objects and defines the methods for
interacting with them. The Application class additionally may
start and update custom data viewers associated with the
data reduction; these should inherit from the Redux Viewer class.
All reduction classes inherit from the generic Reduction class,
which defines the common interface for all reductions: how parameters
are initialized and modified, how each step is called.
Each specific reduction class must then define
each data reduction step as a method that calls the appropriate
algorithm.
The reduction methods may contain any code necessary to accomplish the data reduction step. Typically, a reduction method will contain code to fetch the parameters for the method from the object’s associated Parameters class, then will call an external data reduction algorithm with appropriate parameter values, and store the results in the ‘input’ attribute to be available for the next processing step. If processing results in data that can be displayed, it should be placed in the ‘display_data’ attribute, in a format that can be recognized by the associated Viewers. The Redux GUI checks this attribute at the end of each data reduction step and displays the contents via the Viewer’s ‘display’ method.
Parameters for data reduction are stored as a list of ParameterSet
objects, one for each reduction step. Parameter sets contain the key,
value, data type, and widget type information for every parameter.
A Parameters class may generate these parameter sets by
defining a default dictionary that associates step names with parameter
lists that define these values. This dictionary may be defined directly
in the Parameters class, or may be read in from an external configuration
file or software package, as appropriate for the reduction.
FLITECAM Redux¶
To interface to the FLITECAM pipeline algorithms, Redux defines
the FLITECAMReduction, FLITECAMImagingReduction, and
FLITECAMSpectroscopyReduction as primary reduction classes, with associated
parameter classes FLITECAMParameters, FLITECAMImagingParameters, and
FLITECAMSpectroscopyParameters. [1] Since FLITECAM
data reduction is broadly similar to FORCAST data reduction, FLITECAM
classes all inherit significant functionality from equivalent classes
originally for FORCAST. See Fig. 114 for a sketch of
the Redux classes used by the FLITECAM pipeline.
The FLITECAMReduction class holds definitions for algorithms applicable to
both imaging and spectroscopy data:
Check Headers: calls
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.hdcheckCorrect Nonlinearity: calls
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.lincor
The FLITECAMImagingReduction class inherits from the FLITECAMReduction
class and the FORCASTImagingReduction class and additionally defines
FLITECAM-specific imaging algorithms:
Clip Image: calls
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.clipimg, andsofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.maskbpMake Flat: calls
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.mkflatCorrect Gain: calls
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.gaincorSubtract Sky: calls
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.backsub
The final steps of the pipeline are implemented in the FORCASTImagingReduction
class:
Telluric Correct: calls
sofia_redux.calibration.pipecal_util.apply_tellcorandsofia_redux.calibration.pipecal_util.run_photometryCombine Images: calls
sofia_redux.toolkit.image.coaddFlux Calibrate: calls
sofia_redux.calibration.pipecal_util.apply_fluxcalandsofia_redux.calibration.pipecal_util.run_photometryMake Image Map: calls
sofia_redux.visualization.quicklook.make_image
The FLITECAMSpectroscopyReduction class inherits from the FLITECAMReduction
class and the FORCASTSpectroscopyReduction class. It defines two
FLITECAM-specific algorithms:
Make Spectral Image:
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.mkspecimgCalibrate Flux: calls
sofia_redux.instruments.forcast.getatranandsofia_redux.spectroscopy.fluxcal
All other steps in the pipeline are implemented in FORCASTSpectroscopyReduction:
Stack Dithers: calls
sofia_redux.toolkit.image.combine_imagesMake Profiles: calls
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.rectifyandsofia_redux.spectroscopy.mkspatprofLocate Apertures: calls
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.findaperturesTrace Continuum: calls
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.tracespecSet Apertures: calls
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.getaperturesandsofia_redux.spectroscopy.mkapmaskSubtract Background: calls
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.extspec.col_subbgExtract Spectra: calls
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.extspec.extspecCombine Spectra: calls
sofia_redux.toolkit.image.coaddsofia_redux.instruments.forcast.register_datasets.get_shifts, andsofia_redux.toolkit.image.combine_imagesMake Response: calls
sofia_redux.instruments.forcast.getmodelCombine Response: calls
sofia_redux.toolkit.image.combine_imagesMake Spectral Map: calls
sofia_redux.visualization.quicklook.make_image
The recipe attribute for the reduction class specifies the above steps in the correct order for each pipeline mode.
If an intermediate file is loaded, its product type is identified from the PRODTYPE keyword in its header, and the prodtype_map attribute is used to identify the next step in the recipe. This allows reductions to be picked up at any point, from a saved intermediate file. For more information on the scientific goals and methods used in each step, see the FLITECAM Redux User’s Manual.
The FORCAST reduction classes also contains several helper functions used in
both the FORCAST and FLITECAM pipelines, that
assist in reading and writing files on disk, and identifying which
data to display in the interactive GUI. Display is performed via
the QADViewer class provided by the Redux package. Spectroscopic diagnostic
data is additionally displayed by the MatplotlibViewer class and the
EyeViewer, provided in the sofia_redux.visualization module.
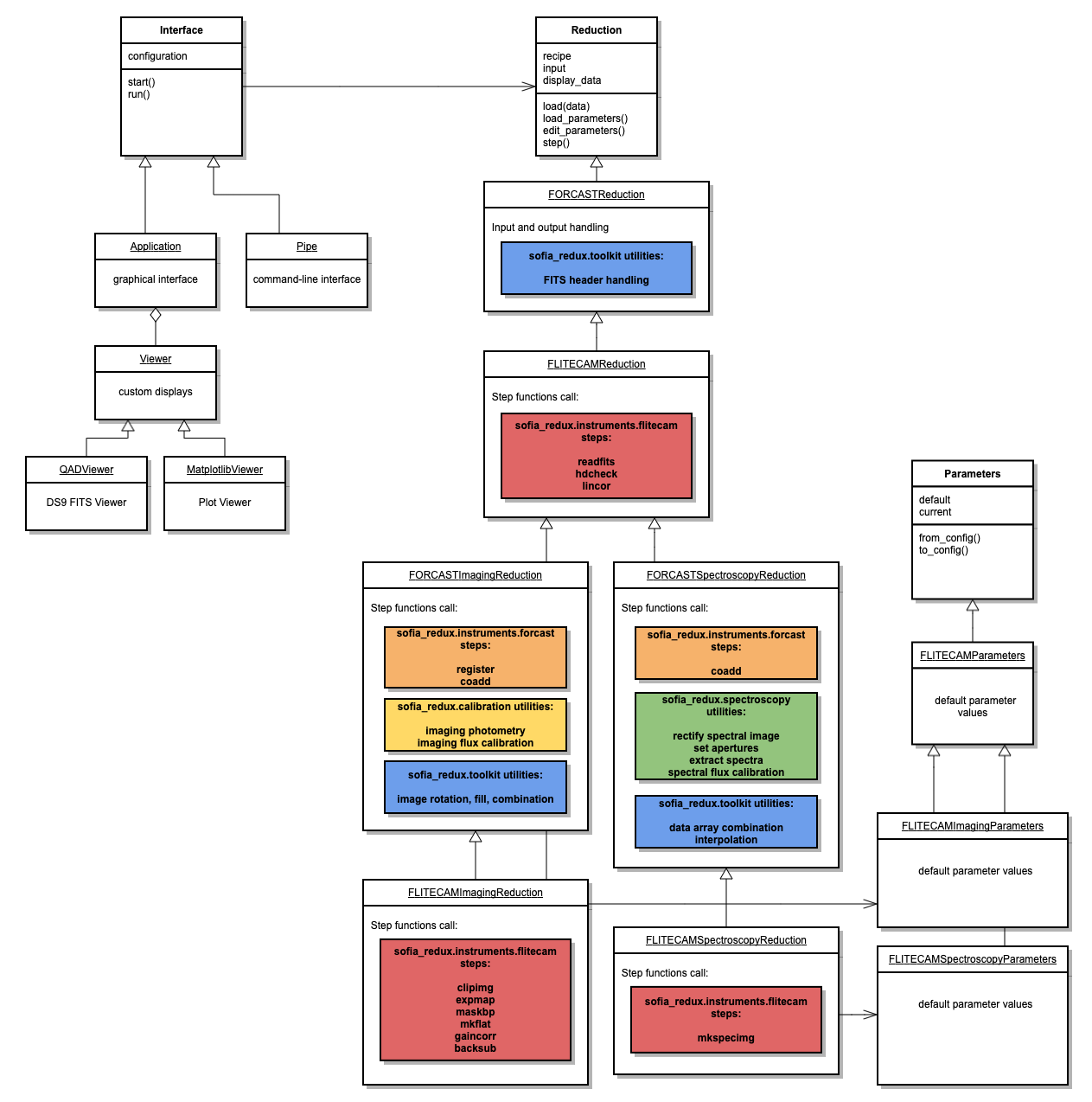
Fig. 114 FLITECAM Redux class diagram.¶
Detailed Algorithm Information¶
The following sections list detailed information on the functions and procedures most likely to be of interest to the developer.
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam¶
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.backsub Module¶
Functions¶
|
Correct flux data for background level. |
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.calcvar Module¶
Functions¶
|
Calculate read and poisson noise from raw FLITECAM images. |
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.clipimg Module¶
Functions¶
|
Clip image to useful portion of the detector. |
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.expmap Module¶
Functions¶
|
Append an exposure map matching the FLUX extension. |
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.gaincor Module¶
Functions¶
|
Correct flux data for gain variations. |
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.getcalpath Module¶
Functions¶
|
Return the path of the ancillary files used for the pipeline. |
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.hdcheck Module¶
Functions¶
|
Validate all keywords in a header against the keywords requirement. |
|
Checks file headers against validity criteria |
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.lincor Module¶
Functions¶
|
Correct input flux data for detector nonlinearity. |
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.maskbp Module¶
Functions¶
|
Identify hot and cold pixels in a data array. |
|
Mask hot and cold bad pixels. |
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.mkflat Module¶
Functions¶
|
Make a flat from dithered sky images. |
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.mkspecimg Module¶
Functions¶
|
Rotate and pair-subtract spectral images. |
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.readfits Module¶
Functions¶
|
Return the data array from the input file. |
sofia_redux.instruments.flitecam.split_input Module¶
Functions¶
|
Split input into categories. |
sofia_redux.instruments.forcast¶
sofia_redux.instruments.forcast.getatran Module¶
Functions¶
Clear all data from the atran cache. |
|
|
Retrieves atmospheric transmission data from the atran cache. |
|
Store atran data in the atran cache. |
|
Retrieve reference atmospheric transmission data. |
sofia_redux.instruments.forcast.getmodel Module¶
Functions¶
Clear all data from the model cache. |
|
|
Retrieves model data from the model cache. |
|
Store model data in the model cache. |
|
Retrieve reference standard model data. |
sofia_redux.instruments.forcast.hdmerge Module¶
Functions¶
|
Merge input headers. |
sofia_redux.instruments.forcast.peakfind Module¶
Functions¶
|
Find peaks (stars) in FORCAST images |
Classes¶
|
Configure and run peak finding algorithm. |
sofia_redux.instruments.forcast.register Module¶
Functions¶
|
Shift an image for coadding using a centroid algorithm |
|
Shift an image for coaddition using a correlation algorithm |
|
Shift an image for coaddition using header information |
|
Shift an image for coaddition using header information |
|
Use dither data to shift_image input image to a reference image. |
sofia_redux.instruments.forcast.register_datasets Module¶
Functions¶
|
Return the pixel offset of a point on header relative to refheader |
|
Returns all shifts relative to the reference set. |
|
Expands an array to a new shape |
|
Shifts an individual data set |
|
Shifts datasets onto common frame |
|
Resize all datasets to the same shape |
|
Registers multiple sets of data to the same frame |
sofia_redux.toolkit¶
sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.base Module¶
Classes¶
|
Convolution class allowing error propagation. |
Class Inheritance Diagram¶
digraph inheritance555cb6bce0 { bgcolor=transparent; rankdir=LR; size=""; "ConvolveBase" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.base.ConvolveBase.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.base.ConvolveBase",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Convolution class allowing error propagation."]; "Model" -> "ConvolveBase" [arrowsize=1.2,arrowtail=empty,dir=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; "Model" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.base.Model.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.base.Model",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Base model Class for fitting N-dimensional data"]; }sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.kernel Module¶
Functions¶
|
Apply a kernel over multiple features |
|
Convolve an N-dimensional array with a user defined kernel or fixed box. |
|
Apply a least-squares (Savitzky-Golay) polynomial filter |
Classes¶
|
Generic convolution with a kernel |
|
Convolution with a box kernel (mean) |
|
Convolve using Savitzky-Golay filter |
Class Inheritance Diagram¶
digraph inheritance7459f88665 { bgcolor=transparent; rankdir=LR; size=""; "BoxConvolve" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.kernel.BoxConvolve.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.kernel.BoxConvolve",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Convolution with a box kernel (mean)"]; "KernelConvolve" -> "BoxConvolve" [arrowsize=1.2,arrowtail=empty,dir=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; "ConvolveBase" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.base.ConvolveBase.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.base.ConvolveBase",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Convolution class allowing error propagation."]; "Model" -> "ConvolveBase" [arrowsize=1.2,arrowtail=empty,dir=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; "KernelConvolve" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.kernel.KernelConvolve.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.kernel.KernelConvolve",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Generic convolution with a kernel"]; "ConvolveBase" -> "KernelConvolve" [arrowsize=1.2,arrowtail=empty,dir=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; "Model" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.base.Model.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.base.Model",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Base model Class for fitting N-dimensional data"]; "SavgolConvolve" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.kernel.SavgolConvolve.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.kernel.SavgolConvolve",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Convolve using Savitzky-Golay filter"]; "ConvolveBase" -> "SavgolConvolve" [arrowsize=1.2,arrowtail=empty,dir=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; }sofia_redux.toolkit.convolve.filter Module¶
Functions¶
|
Apply Savitzky-Golay filter to an array of arbitrary features |
|
Creates the correct windows for given order and samples |
|
Edge enhancement Sobel filter for n-dimensional images. |
sofia_redux.toolkit.fitting.fitpeaks1d Module¶
Functions¶
|
Simple convenience lookup to get width parameter name for various models. |
|
Creates the object fitting a model to data |
|
A simple wrapper to fit model to the data |
|
Convolve a model with a box (or another model) |
|
Create the |
|
Perform an initial search for peaks in the data |
|
Return a background model with initialized parameters |
|
Refine the initial fit and return a set of models |
|
Fit peaks (and optionally background) to a 1D set of data. |
|
Default data preparation for |
|
Default peak guess function for |
sofia_redux.toolkit.fitting.polynomial Module¶
Functions¶
|
Returns exponents for given polynomial orders in arbitrary dimensions. |
|
Create a system of linear equations to solve n-D polynomials |
|
Create a system of linear equations |
|
Linear equation solution by Gauss-Jordan elimination and matrix inversion |
|
Evalulate polynomial coefficients at x |
|
Evaluate a polynomial in multiple features |
|
Calculate the zeroth order polynomial coefficients and covariance |
|
Fit a polynomial to data samples using linear least-squares. |
|
Fit a polynomial to data samples using Gauss-Jordan elimination. |
|
Solve for polynomial coefficients using non-linear least squares fit |
|
Fits polynomial coefficients to N-dimensional data. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Least squares polynomial fit to a surface |
|
Evaluate 2D polynomial coefficients |
|
Interpolate 2D data using polynomial regression (global) |
Classes¶
|
Fits and evaluates polynomials in N-dimensions. |
Class Inheritance Diagram¶
digraph inheritance812590e9a1 { bgcolor=transparent; rankdir=LR; size=""; "Model" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.base.Model.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.base.Model",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Base model Class for fitting N-dimensional data"]; "Polyfit" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.fitting.polynomial.Polyfit.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.fitting.polynomial.Polyfit",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Fits and evaluates polynomials in N-dimensions."]; "Model" -> "Polyfit" [arrowsize=1.2,arrowtail=empty,dir=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; }sofia_redux.toolkit.image.adjust Module¶
Functions¶
|
Shift an image by the specified amount. |
|
Rotate an image. |
|
Rebins an array to new shape |
|
Shifts an image by x and y offsets |
|
Replicates IDL rotate function |
|
Un-rotates an image using IDL style rotation types |
|
Return the pixel offset between an image and a reference |
|
Upsampled DFT by matrix multiplication. |
sofia_redux.toolkit.image.coadd Module¶
Functions¶
|
Coadd total intensity or spectral images. |
sofia_redux.toolkit.image.combine Module¶
Functions¶
|
Combine input image arrays. |
sofia_redux.toolkit.image.fill Module¶
Functions¶
|
|
|
|
|
Interpolates over image using a mask. |
|
Fills in NaN values in an image |
|
Clip a polygon to a square unit pixel |
|
Finds all pixels at least partially inside a specified polygon |
|
Uses the shoelace method to calculate area of a polygon |
|
Get pixel weights - depreciated by polyfillaa |
sofia_redux.toolkit.image.resize Module¶
Functions¶
|
Replacement for |
sofia_redux.toolkit.image.smooth Module¶
Functions¶
|
Quick and simple cubic polynomial fit to surface - no checks |
|
Returns the coefficients necessary for bicubic interpolation. |
|
|
|
Fit a plane to distribution of points. |
|
Fits a smooth surface to data using J. |
sofia_redux.toolkit.image.utilities Module¶
Functions¶
|
Convert from |
|
Allow translation of modes for scipy versions >= 1.6.0 |
|
Clip the array to the range of original values. |
|
A drop in replacement for |
sofia_redux.toolkit.image.warp Module¶
Functions¶
|
Warp data using transformation defined by two sets of coordinates |
|
Performs polynomial spatial warping |
|
Warp an image by mapping 2 coordinate sets with a polynomial transform. |
|
Check if a transform is homographic. |
|
Apply a metric transform to the supplied coordinates. |
|
Apply coefficients to polynomial terms. |
|
Estimate the polynomial transform for (x, y) coordinates. |
|
Apply the warping between two sets of coordinates to another. |
|
Warp the indices of an array with a given shape using a polynomial. |
|
Warp an n-dimensional image according to a given coordinate transform. |
Classes¶
|
Initialize a polynomial transform. |
Class Inheritance Diagram¶
digraph inheritance2c28666683 { bgcolor=transparent; rankdir=LR; size=""; "ABC" [URL="https://docs.python.org/3/library/abc.html#abc.ABC",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Helper class that provides a standard way to create an ABC using"]; "PolynomialTransform" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.image.warp.PolynomialTransform.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.image.warp.PolynomialTransform",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top"]; "ABC" -> "PolynomialTransform" [arrowsize=1.2,arrowtail=empty,dir=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; }sofia_redux.toolkit.interpolate.interpolate Module¶
Functions¶
|
Shift an equally spaced array of data values by an offset |
|
Interpolate values containing NaNs |
|
Perform cubic spline (tensioned) interpolation |
|
Perform a sinc interpolation on a data set |
|
Perform linear interpolation at a single point. |
|
Perform linear interpolation at a single point with error propagation. |
|
Perform linear interpolation of errors |
|
Propagate errors using Delaunay triangulation in N-dimensions |
|
Propagate errors using linear interpolation in N-dimensions |
|
Find the effective index of a function value in an ordered vector with NaN handling. |
|
Finds the effective index of a function value in an ordered array. |
Classes¶
|
Fast interpolation on a regular grid |
Class Inheritance Diagram¶
digraph inheritanceb8ee21f950 { bgcolor=transparent; rankdir=LR; size=""; "Interpolate" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.interpolate.interpolate.Interpolate.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.interpolate.interpolate.Interpolate",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Fast interpolation on a regular grid"]; }sofia_redux.toolkit.stats.stats Module¶
Functions¶
|
Determines the outliers in a distribution of data |
|
(Robustly) averages arrays along arbitrary axes. |
|
Combines a data set using median |
|
Computes statistics on a data set avoiding deviant points if requested |
|
Computes a mask derived from data Median Absolute Deviation (MAD). |
sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.base Module¶
Classes¶
|
Base model Class for fitting N-dimensional data |
Class Inheritance Diagram¶
digraph inheritanced18b721993 { bgcolor=transparent; rankdir=LR; size=""; "Model" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.base.Model.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.base.Model",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Base model Class for fitting N-dimensional data"]; }sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.fits Module¶
Functions¶
|
Insert or replace a keyword and value in the header |
|
Add HISTORY message to a FITS header before the pipeline. |
|
Make a function to add HISTORY messages to a header, prefixed with a string. |
|
Retrieve the data and header from a FITS file |
|
Returns the header of a FITS file |
|
Returns the data from a FITS file |
|
Convert a FITS header to an array of strings |
|
Convert an array of strings to a FITS header |
|
Returns the HDUList from a FITS file |
|
Write a HDULists to disk. |
|
Get a key value from a header. |
|
Context manager to temporarily set the log level. |
|
Order headers based on contents. |
|
Merge input headers. |
sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.func Module¶
Functions¶
|
Check for 'truthy' values. |
|
Check for valid numbers. |
|
Returns list sorted in a human friendly manner |
|
Check if a file exists, and optionally if it has the correct permissions. |
|
Convert a header datestring to seconds |
|
Convert a string to an int or float. |
|
Returns a slice of an array in arbitrary dimension. |
|
Sets a value to a valid number type |
|
Gaussian model for curve_fit |
|
Broadcast an array to the desired shape. |
|
Recursively update a dictionary |
|
|
|
|
|
Taylor expansion generator for Polynomial exponents |
|
Convert a number of bytes to a string with correct suffix |
|
Remove any samples containing NaNs from sample points |
|
Return a byte array the same size as the input array. |
|
Generate a 2-D Julia fractal image |
|
Derive a mask to trim NaNs from an array |
|
Emulates the behaviour of np.nansum for NumPy versions <= 1.9.0. |
sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.multiprocessing Module¶
Functions¶
|
Returns the maximum number of CPU cores available |
|
Return the actual number of cores to use for a given number of jobs. |
|
Return a valid number of jobs in the range 1 <= jobs <= max_cores. |
|
Process a series of tasks in serial, or in parallel using joblib. |
|
Pickle a object and save to the given filename. |
|
Unpickle a string argument if it is a file, and return the result. |
|
Pickle a list of objects to a temporary directory. |
|
Restore pickle files to objects in-place. |
Return whether the process is running in the main thread. |
|
|
Context manager to temporarily log messages for unique processes/threads |
|
Context manager to output log messages during multiprocessing. |
|
Remove all temporary logging files/directories and handle log records. |
|
Return the results of the function in multitask and save log records. |
|
Store the log records in a pickle file rather than emitting. |
|
Wrap a function for use with |
Classes¶
A log handler for multitask. |
Class Inheritance Diagram¶
digraph inheritance7a3b669de2 { bgcolor=transparent; rankdir=LR; size=""; "Filterer" [fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",tooltip="A base class for loggers and handlers which allows them to share"]; "Handler" [URL="https://docs.python.org/3/library/logging.html#logging.Handler",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Handler instances dispatch logging events to specific destinations."]; "Filterer" -> "Handler" [arrowsize=1.2,arrowtail=empty,dir=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; "MultitaskHandler" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.multiprocessing.MultitaskHandler.html#sofia_redux.toolkit.utilities.multiprocessing.MultitaskHandler",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="A log handler for multitask."]; "Handler" -> "MultitaskHandler" [arrowsize=1.2,arrowtail=empty,dir=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; }sofia_redux.spectroscopy¶
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.binspec Module¶
Functions¶
|
Bin a spectrum between lmin and lmax with bins delta wide |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.earthvelocity Module¶
Functions¶
|
Find the radial LSR velocity towards sky coordinates. |
|
Calculate the Cartesian velocity of the Sun. |
|
Provide velocities of the Earth towards a celestial position. |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.extspec Module¶
Functions¶
|
Fit background to a single column. |
|
Extracts spectra from a rectified spectral image. |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.findapertures Module¶
Functions¶
|
Determine the position of the aperture(s) in a spatial profile. |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.fluxcal Module¶
Functions¶
|
Get pixel shift between flux and correction curve. |
|
Calibrate and telluric correct spectral flux. |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.getapertures Module¶
Functions¶
|
Determine aperture radii for extraction. |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.getspecscale Module¶
Functions¶
|
Determines the scale factors for a _stack of spectra |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.mkapmask Module¶
Functions¶
|
Constructs a 2D aperture mask. |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.mkspatprof Module¶
Functions¶
|
Construct average spatial profiles. |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.radvel Module¶
Functions¶
|
Calculate the expected extrinsic radial velocity wavelength shift. |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.readflat Module¶
Functions¶
|
Reads a Spextool flat field FITS image |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.readwavecal Module¶
Functions¶
|
Read a Spextool wavecal file |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.rectify Module¶
Functions¶
|
Construct average spatial profiles over multiple orders |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.rectifyorder Module¶
Functions¶
|
Given arrays of x and y coordinates, interpolate to defined grids |
|
Trim rows and columns from the edges of the coordinate arrays. |
|
Construct average spatial profiles for a single order |
|
Update a FITS header with spectral WCS information. |
|
Construct average spatial profiles for a single order |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.smoothres Module¶
Functions¶
|
Smooth a data to a constant resolution |
sofia_redux.spectroscopy.tracespec Module¶
Functions¶
|
Trace spectral continua in a spatially/spectrally rectified image. |
sofia_redux.calibration¶
sofia_redux.calibration.pipecal_applyphot Module¶
Calculate aperture photometry and update FITS header.
Functions¶
|
Calculate photometry on a FITS image and store results to FITS header. |
sofia_redux.calibration.pipecal_calfac Module¶
Calculate a calibration factor from a standard flux value.
Functions¶
|
Calculate the calibration factor for a flux standard. |
sofia_redux.calibration.pipecal_config Module¶
Calibration configuration.
Functions¶
|
Parse all reference files and return appropriate configuration values. |
|
Read response files. |
sofia_redux.calibration.pipecal_fitpeak Module¶
Fit a 2D function to an image.
Functions¶
|
Function for an elliptical Gaussian profile. |
|
Function for an elliptical Lorentzian profile. |
|
Function for an elliptical Moffat profile. |
|
Fit a peak profile to a 2D image. |
sofia_redux.calibration.pipecal_photometry Module¶
Fit a source and perform aperture photometry.
Functions¶
|
Perform aperture photometry and profile fits on image data. |
sofia_redux.calibration.pipecal_rratio Module¶
Calculate response ratio for atmospheric correction.
Functions¶
|
Calculate the R ratio for a given ZA and Altitude or PWV. |
sofia_redux.calibration.pipecal_util Module¶
Utility and convenience functions for common pipecal use cases.
Functions¶
|
Robust average of zenith angle from FITS header. |
|
Robust average of altitude from FITS header. |
|
Robust average of precipitable water vapor from FITS header. |
|
Estimate the position of a standard source in the image. |
|
Add calibration-related keywords to a header. |
|
Add photometry-related keywords to a header. |
|
Retrieve a flux calibration factor from configuration. |
|
Apply a flux calibration factor to an image. |
|
Retrieve a telluric correction factor from configuration. |
|
Apply a telluric correction factor to an image. |
|
Run photometry on an image of a standard source. |
sofia_redux.calibration.pipecal_error Module¶
Base class for pipecal errors.
Classes¶
A ValueError raised by pipecal functions. |
sofia_redux.visualization¶
sofia_redux.visualization.quicklook Module¶
Functions¶
|
Generate a map image from a FITS file. |
|
Generate a plot of spectral data. |
sofia_redux.visualization.redux_viewer Module¶
Classes¶
Redux Viewer interface to the Eye of SOFIA. |
Class Inheritance Diagram¶
digraph inheritance28e1a7d94e { bgcolor=transparent; rankdir=LR; size=""; "EyeViewer" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.visualization.redux_viewer.EyeViewer.html#sofia_redux.visualization.redux_viewer.EyeViewer",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Redux Viewer interface to the Eye of SOFIA."]; "Viewer" -> "EyeViewer" [arrowsize=1.2,arrowtail=empty,dir=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; "Viewer" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.pipeline.viewer.Viewer.html#sofia_redux.pipeline.viewer.Viewer",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Parent class for Redux data viewers."]; }sofia_redux.visualization.controller Module¶
Standalone front-end for Eye of SOFIA display tool.
Functions¶
|
The Eye of SOFIA spectral viewer. |
|
Parse command line arguments. |
|
Check arguments for validity. |
sofia_redux.visualization.eye Module¶
Classes¶
|
Run the Eye of SOFIA. |
Class Inheritance Diagram¶
digraph inheritancebb54a4d2b2 { bgcolor=transparent; rankdir=LR; size=""; "Eye" [URL="../../../api/sofia_redux.visualization.eye.Eye.html#sofia_redux.visualization.eye.Eye",fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=10,height=0.25,margin=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="Run the Eye of SOFIA."]; }sofia_redux.pipeline¶
The Redux application programming interface (API), including the FLITECAM
interface classes, are documented in the sofia_redux.pipeline package.
Appendix A: Pipeline Recipe¶
This JSON document is the black-box interface specification for the FLITECAM Redux pipeline, as defined in the Pipetools-Pipeline ICD.
{
"inputmanifest" : "infiles.txt",
"outputmanifest" : "outfiles.txt",
"env" : {
"DPS_PYTHON": "$DPS_SHARE/share/anaconda3/envs/flitecam/bin"
},
"knobs" : {
"REDUX_CONFIG" : {
"desc" : "Redux parameter file containing custom configuration.",
"type" : "string",
"default": "None"
}
},
"command" : "$DPS_PYTHON/redux_pipe infiles.txt -c $DPS_REDUX_CONFIG"
}